Psalm 18 Overview
Welcome to the Overview of Psalm 18
This page will introduce and provide orientation to Psalm 18 as a whole. It includes the following sections:
Introduction to Psalm 18
Author
- David
Book
- Book 1 of the Psalter (Chapters 1–41)
Psalm 18: A Brief Summary
- In Psalm 18, the psalmist goes through the depths of despair, due to approaching threats of death and destruction, but he finishes in the heights of triumph as every last enemy of the psalmist falls defeated at his feet. In the end, enthusiastic praise bursts forth from the psalmist's mouth: “YHWH lives! And my rock is blessed! The God who rescues me is exalted!”
"YHWH: My strength and deliverer" This title is a memorable phrase that helps remember the unique character and content of this psalm.
- The phrase, “YHWH: My strength and deliverer,” summarizes both what the psalmist needs as he faces difficulty, and the solution to his crisis. David was in desperate need of strength and deliverance, and YHWH supplied both in abundance. He equipped David with strength and delivered him from all his enemies. YHWH responded to David’s love with covenant loyalty that delivered him from all trouble, just when he needed it.
Purpose The Purpose was the psalmist's probable intent or reason for writing this psalm.
- To express confidence in YHWH as the strength and deliverer of his loyal ones.
Content The Content is a concise summary of the whole psalm's content.
- YHWH shows his loyalty toward David (v. 50) by being perfectly just (vv. 26-27). David shows his love towards YHWH (v. 2) by being righteous and faithful (vv. 21-250. That's why YHWH delivers David by strengthening him (vv. 31-43) and fighting cosmic forces on his behalf (vv. 8-20).
Message The Message is the main idea the psalmist probably wanted the audience to remember upon or after hearing the psalm.
- YHWH treats people according to their loyalty.
Psalm 18 At-a-Glance
These sections divide the content of the psalm into digestible pieces , and are determined based on information from many of our layers, including Semantics, Poetics, and Discourse. The columns, left to right, contain: the verse numbers; the main title of the section; a brief summary of the content of that section (quote marks indicate the text is taken directly from the English text of the psalm (as per our Close-but-Clear translation); and an icon to visually represent and remember the content.
|
v. 1 For the director By YHWH's servant, David, who recited the words of this song to YHWH when YHWH had rescued him from the palm of all his enemies and from the hand of Saul. |
Superscription | |||
|
v. 2 And he said, “I shall keep loving you, YHWH, my strength. |
David's distress |
“I love YHWH, my deliverer and my strength!” David cries out in distress and YHWH hears |
Distress |
|
| v. 3 YHWH is my cleft and my fortress and my rescuer. My God is my rock, in him do I seek protection, my shield and horn of my deliverance, my fortified tower and my refuge, my deliverer, who delivers me from violence. | ||||
| v. 4 I cry out to YHWH, since he is praiseworthy, and I am delivered from my enemies. | ||||
| v. 5 The breaker waves of Death surrounded me. And the torrents of No Return began to overwhelm me. | ||||
| v. 6 The cords of the World of the Dead entangled me. Death's traps rushed upon me. | ||||
| v. 7 In my distress I cry out to YHWH. And to my God do I cry for help. He hears my cry from his temple. And my cry for help before him comes into his ears. | ||||
|
v. 8 And the earth quivered and quaked. And the mountains' foundations began to shake. And they trembled. For he had become angry. |
YHWH delivers David |
YHWH prepares for battle
YHWH's battle on David's behalf YHWH's victory over many waters
|
Awe |
|
| v. 9 Smoke went up because of his snarl. And a fire from his mouth began to consume. Coals burned from him. | ||||
| v.10 And he bent down the heavens and descended. And a dark smog was beneath his feet. | ||||
| v.11 And he mounted a Cherub and began to fly. And he flew swiftly upon the wings of the wind. | ||||
| v.12 He made darkness his cover. [He made darkness] his canopy around him, the sieve of water, thick clouds of the skies. | ||||
| v.13 Because of the brightness before him, hail and coals of fire passed. | ||||
| v.14 And YHWH thundered in the heavens. And the Most High began to raise his voice. | ||||
| v.15 And he shot his arrows, and dispersed them. And [he shot his] glittering arrows, and routed them. | ||||
|
v.16 And the ocean floor appeared. And the foundations of the world were revealed because of your rebuke, YHWH, because of the blast of the wind of your anger. |
Relief |
|||
| v.17 He stretched forth his hand from on high and took me. He pulled me out from many waters. | ||||
| v.18 He rescued me from my strong enemy. And [he rescued me] from those who hate me. For they were too powerful for me. | ||||
| v.19 They rushed upon me at the time of my calamity. And YHWH was the one in whom I trusted. | ||||
| v.20 And he brought me out into relief. He delivered me. For he is pleased with me. | ||||
|
v.21 YHWH deals well with me according to my righteousness. He repays me according to the cleanliness of my hands. |
YHWH vindicates David |
YHWH rewards David because he has kept his ways. |
Confidence |
|
| v.22 For I have kept the ways of YHWH. And I have not turned from my God towards wicked ways. | ||||
| v.23 For all of his rules are before me. And I will not turn his decrees away from me. | ||||
| v.24 And I have become blameless before him. And I have kept myself from committing iniquity. | ||||
| v.25 And YHWH has repaid me according to my righteousness, according to the cleanliness of my hands before his eyes. | ||||
|
v.26 You act faithfully with a faithful person. You act blamelessly with a blameless person. |
YHWH saves the humble, but humbles the prideful |
Well-being |
||
| v.27 You act with purity with one who purifies himself. And with a twisted person you act wittily. | ||||
| v.28 For you save a humble people. And you bring down eyes that look down on others. | ||||
| v.29 For you light my lamp, YHWH. My God gives light to my darkness. | ||||
| v.30 For by you I can rout an army. And by my God I can scale a wall. | ||||
|
v.31 God—His way is perfect. The sayings of YHWH are true. He is a shield to all those who take refuge in him. |
David defeats his enemies |
YHWH prepares David for battle
David's battle in YHWH's strength David's victory over his enemies
|
Triumph |
|
| v.32 For who is God besides YHWH? And who is a rock besides our God, | ||||
| v.33 the God who arms me with strength and makes my endeavor secure? | ||||
| v.34 He makes my feet like those of deer. And he causes me to stand upon my heights. | ||||
| v.35 He trains my hands for war. And he strengthens my arms with a bow of bronze. | ||||
| v.36 And you give me the shield of your victory. And your right hand supports me. And your help makes me great. | ||||
| v.37 You enlarged my steps underneath me. And my ankles did not falter. | ||||
| v.38 I chased my enemies and I overtook them. And I would not relent until their destruction. | ||||
| v.39 I violently beat them, and they could not stand. They fell beneath my feet. | ||||
| v.40 And so you armed me with strength for war. You make those who rise up against me kneel underneath me. | ||||
| v.41 And you have made my enemies retreat from me. And as for those who hate me, I wipe them out. | ||||
| v.42 They cry out for help, and there is no rescuer. [They cry out for help] to YHWH, and he has not answered them. | ||||
| v.43 And I crush them like the dust on the road. I beat them like the mud of the streets. | ||||
| v.44 You will deliver me from people's indictments. You will make me head of nations. A people I do not know will serve me. |
David praises YHWH for victory |
“You will indeed exalt me over those who rise up against me”
“I shall praise you, YHWH!”
|
Confidence |
|
| v.45 As soon as they hear rumors of me they will show obedience to me. Foreigners will submit to me. | ||||
|
v.46 Foreigners will lose heart and tremble from their fortresses. |
||||
| v.47 YHWH lives! And my rock is blessed! And the God of my rescue is exalted! | ||||
| v.48 God—who gives me vengeance, and subdues peoples underneath me. | ||||
| v.49 You who deliver me from my enemies will indeed exalt me over those who rise up against me. You will rescue me from the violent man. | ||||
| v.50 Therefore I shall praise you among the nations, YHWH! And I shall sing praise to your name, | ||||
| v.51 you who makes the deliverance of his king spectacular, and performs acts of loyalty for his anointed one, for David, and for his seed, forever.” | ||||
Background Orientation for Psalm 18
Following are the common-ground assumptionsCommon-ground assumptions include information shared by the speaker and hearers. In our analysis, we mainly use this category for Biblical/Ancient Near Eastern background. which are the most helpful for making sense of the psalm.
- David is in a binding relationship to YHWH (a “covenant”) whereby commandments and protection are exchanged for obedience (Exod 20:6; Deut 5:10; 6:5; 7:9; 1 Kg 3:3; Neh 1:5).
- In the Psalms, the king was YHWH's representative on earth (cf. Psalm 2:11–12; Keel 1997, 246–247), such that The king's enemies are God's enemies: "The Israelite king's view of his enemies can be compared with that of other sacred kings. The Assyrian king, for example, considered his enemies as enemies of his gods, guilty of impious rebellion” (Eaton 1975, 141).
- YHWH is sometimes portrayed as the Divine Warrior in battle (see Longman and Reid 1995, 31–48) of the Ancient Near East. The Divine Warrior was a common creation myth in Syria-Palestine whereby, crucially, “a Divine Warrior goes forth to battle the chaotic monsters, variously called Sea, Death, Leviathan, Tannin; (2) the world of nature responds to the wrath of the Divine Warrior and the forces of chaos are defeated...” (see Oden 1992, 1164).
- God's manifestation of his presence usually took the form of a thunderstorm (see Hiebert 1992, 508; Walton 2009, 333; COS I:260n.160; Josh 10:11; Job 38:22–23; Isa 30:30).
- Due to its association with death and Sheol (cf. Yuan 2023, 127–128), water was a symbol of the wicked and of enemy armies (May 1955).
- The winds hailed from four directions and were thought to be produced by divine wings, thus the earth is said to have “wings” (Isa 11:12; Ezek 7:2) (see Noegel 2017, 19–20). “Wings” therefore became conceptually linked with, and virtually a byword for, directions.
- In Biblical Cosmology, the earth was perceived as a a flat disk that sat above the Chaos-waters (see Keel 1997, 40). It was upheld by its “foundations” (Isa 24:18; Jer. 31:37; Micah 6:2, etc.), which were most likely mountains (cf. Deut 32.22). Thus the “foundations” of the earth and the “foundations of the mountains” are co-referential. Heaven was perceived of as a solid vault from which the sun, moon and stars hung (Gen 1.14–17; see Bartelmus 2006, 2011). This vault (cf. Ps 19:1) kept the chaos waters from above from flooding the earth. Above the chaos-waters from above, in the highest heavens, sat the Lord (Ps 29:10).
Background Situation for Psalm 18
The background situation is the series of events leading up to the time in which the psalm is spoken. These are taken from the story triangle – whatever lies to the left of the star icon.
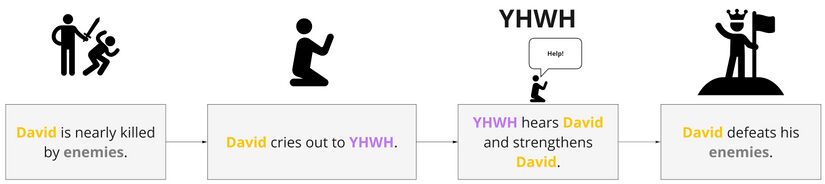
Participants in Psalm 18
There are 5 participants/characters in Psalm 18
| YHWH |
| YHWH's right hand |
| YHWH's help |
| YHWH's name |
| "My strength" (v. 2) |
| “My cleft” (v. 3) |
| “My fortress” (v. 3) |
| “My rescuer” (v. 3) |
| “My God” (v. 3) |
| “My rock” (v. 3) |
| “My shield” (v. 3) |
| “Horn of my deliverance” (v. 3) |
| “My fortified tower” (v. 3) |
| “My refuge” (v. 3) |
| “My deliverer” (v. 3) |
| “The most high” (v. 14) |
| "The one who arms me with strength” (v. 33) |
| "Rescuer" (v. 42) |
| "The one who makes the deliverance of his king spectacular" (v. 51) |
| "The one who performs acts of loyalty for his anointed one" (v. 51) |
| God's way |
| God's rules (v. 23) |
| God's decrees (v. 23) |
| The sayings of YHWH (v. 31) |
| YHWH's anger |
| Smoke (v. 9) |
| Fire (v. 9) |
| Coals (v. 9) |
| Hail (v. 13) |
| God's rebuke (v. 16) |
| The blast of the wind of his anger (v. 16) |
| David |
| "YHWH's servant" (v. 1) |
| "[God's] King" (v. 51) |
| "[God's] Anointed" (v. 51) |
| Cry (for help) |
| "My sword" (v. 7) |
| David's seed |
| A faithful person |
| A blameless person (v. 26) |
| One who purifies himself (v. 27) |
| A humble people (v. 28) |
| Those who take refuge in him (v. 31) |
| Enemies |
| “those who hate me” (v. 18) |
| "those who rise up against me" (v. 40) |
| The violent man |
| Saul |
| Forces of Death |
| Death's breaker waves (v. 5) |
| Torrents of No Return (v. 6) |
| Cords of the World of the Dead (v. 6) |
| Death's traps (v. 6) |
| Waters (v. 17) |
| Sinful people |
| A twisted person (v. 27) |
| Eyes that look down on others (v. 27) |
| A people I do not know |
| "Nations" (vv. 44, 50) |
| “Foreigners” (vv. 45, 46) |
| The Earth |
| The mountains' foundations |
| The ocean floor |
- A faithful person: This and the related generic referring expressions appear in vv. 26–31. They function to illustrate the principle on the basis of which God acts on behalf of the Psalmist: “acts beget consequences” (see Hubbard 1982), that is, God shows himself to an individual in a way commensurate with their actions. That the Psalmist counts himself among these “faithful persons” is suggested by both participants “taking refuge” (חסה) in YHWH (see vv. 3, 31) and the suffix in v. 32.
- YHWH's anger and its related participants (vv. 9–13, 16) all serve as manifestations of God's anger (see Hupfeld 1885, 288). They function together with the earth and Death's waters and other terrestrial participants to mark the turning points in the plot. The earth reacting to God's anger is an instance of “theophany”, that is, the manifestation of God. In essence, in this section of the psalm God “shows up” and thus effects a change in the Psalmist's situation. Similarly, God uses his “rebuke” to defeat death's waters in v. 16. We are told that the rebuke is the wind of God's “anger” in v. 16, and so we have grouped it with the other theophany elements.